Coaching 101: Myths busted and advice for using a coaching approach
Do you want to help your team members improve their performance? Do your one-to-one meetings often end up with you giving all the answers and telling them what to do? Do you want your team to be more self-sufficient and empowered?
If the answer to any of the above is yes, then I suggest you learn how to coach. Increasingly seen as an essential management tool, coaching supports people to give their very best regardless of their current performance level. Coaching is focussed on helping them find solutions themselves, rather than the manager providing direction or advice. As a coach, and a trainer of coaches, I’m going to share with you some of my key ideas on why all managers and leaders should be coaching.
 1. Coaching myths
1. Coaching myths
We’ll cover aspects of how to coach later, but first, let’s look at some of the reasons why managers don’t coach, and debunk these myths.
Myth 1: “It takes too long; it takes less time if I just tell them the answer or what to do.”
You may worry that coaching is too time consuming, but it takes no more time overall than many other management practices. Crucially coaching builds capacity in your team to resolve their own issues – or to come to you with solutions, rather than questions. This saves you time in the medium to long run
Myth 2: “I’m not a professional coach, surely an external person needs to do this work?”
While there is real value in independent coaching, anyone can add a coaching approach to their management toolkit. I’ve trained hundreds in coaching skills, and you’d be surprised how quickly people can take it on board. David Rock defines coaching as ‘the art and science of facilitating positive change’ – and if you think about it, that’s what good managers are all about. The aim of coaching, and the skills you need, are aligned with being a positive and supportive manager: meeting people where they are, then helping them build on their skills, strengths and experiences, addressing shortcomings, finding solutions and identifying strategies to meet agreed targets.
Myth 3: “I’m the manager, I have the right answers, I should always share them.”
You should if there is only one right answer. But allowing your colleagues to maintain ownership, think issues through and work out their own solutions helps to get the best from your people. If you focus on goals and outcomes, your team can be more creative. Sir John Whitmore argues that coaching encourages acceptance of responsibility, which results in a commitment, in turn optimising employees’ performance.
A coaching approach helps establish boundaries around their responsibility for delivering outcomes and resolving issues. Your role is to work with people not for them – helping them work towards solutions rather than micro-managing. It helps when people own their goals.
Telling people the right answers isn’t always effective. Think about training sessions: a significant U.S. study found that the application of learning following a training course was around 22%. The majority simply didn’t put anything into practice. But when training was combined with coaching or some sort of a follow-up, it really helped people put their learning into practise. Suddenly, application went up to 90% – so with an approach of coaching rather than telling you could generate a much better return on your time investment.
2. When to use a coaching approach
PWC’s Global Coaching Study for the International Coach Federation found that coaching creates improvements in areas such as self-confidence, relationships, communication skills, work-life balance, work performance, business management and team effectiveness.
So, is there any occasion when you would not want your team to have those benefits? I’d encourage you to make coaching part of your daily management skills – but especially when there are high stakes pieces of work, big projects, or issues where you’re carrying an awful lot of responsibility.
Coaching can be delivered just in time; you can talk about a project just as it arises. Coaching is targeted, it can be specific to your organisation and the type of work or individual that you are talking to. It can build on their experience, knowledge, and skills while addressing their specific challenges.
By adding a coaching approach to your practice you can look forward to reaping its many personal and organisational benefits.
3. What a coaching approach looks like
Now we’re going to consider how you would start coaching. You can coach anytime, anywhere. Your coaching conversations don’t need to be formal or take more than a few minutes. It is however distinguished from other management activity by two key points:
- it is solution-focussed
- it leaves ownership and accountability with the staff member or coachee.
To achieve this, coaching involves asking insightful questions and providing reflection without giving advice or direction.
3.1 Start with the outcome
Start conversations with ‘what do we want to achieve?’, ‘what do you need?’. Encourage your staff member to articulate where they are aspiring to be or what an ideal outcome would look like.
Then you look at the current situation: ‘This is our goal, and this is where we are at the moment. Let’s talk about how we bridge that gap.’
Next, encourage the coachee to come up with potential solutions or options. Rather than providing advice, ask questions to help them work issues out for themselves: ‘What options do you have?’ ‘What do we need to do to make this project a success?’ ‘How are you going to marshal your skills, experience, and resources to achieve it?’ and the magic coaching question: ‘What else?’ Aim for as many options as they can gather – I often find that the really innovative solutions only emerge once I’ve exhausted all the obvious ideas.
Ensure that there is a specific set of outcomes or actions from the coaching conversation. The coachee needs to choose and commit to their own next step to draw real benefit from this approach.
This basic process I’ve described has been worked up into a number of coaching models. There’s not much difference between them beyond which acronym you prefer.
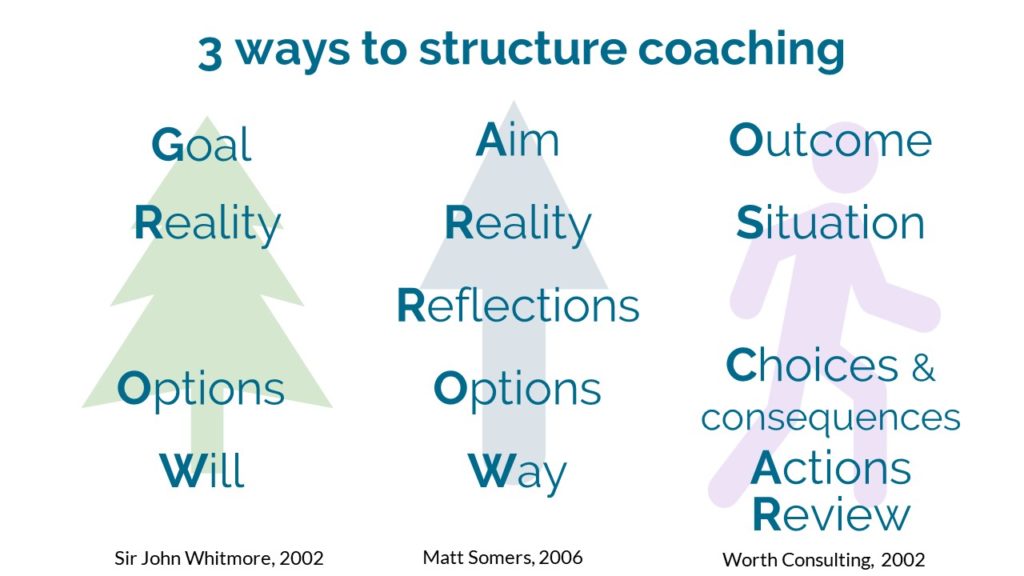
3.2 It is not about you – ownership and accountability belong with the coachee
In coaching the question is always, ‘what are you going to do’, and then ‘what support might you need to succeed’? Accountability and ownership rests with the coachee or individual whose job or project you are discussing.
Your role is to facilitate their thinking, not to solve the team member’s issues, or do their job for them. Understanding this distinction is remarkably freeing and allows for better quality conversations. It will be tough at first, but try hard not to be directive.
Listen to the other person, rather than your thoughts about how you might respond. What is really important to them? What are their challenges? What opportunities are they seeing? What next steps do they want to take?
When encouraged to come up with our own solutions, we maintain ownership and accountability, and feel much more motivated to follow through than when we are told what to do.
3.3 Provide support and challenge
Provide support and help where it is needed. Ask your team member to articulate what they see as the main challenge in a particular project and how you can support them in overcoming it.
Encourage them to identify the resources available to them; or similar situations or tasks where they have previously been successful.
Praise people for difficulties they’ve chosen to tackle, for taking ownership and accountability or for doing a great job of resolving their own issues.
Also provide constructive challenge. If you hear ‘We can never do that because…’ ask them, ‘Are you sure? Can you tell me what it would take for us to actually be able to do it? Could we do something differently to enable us to achieve this?’ Challenging is often a crucial part of coaching conversations.
4. Coaching is a crucial management skill that you should have
So you can see that coaching has wide-ranging benefits for your team and you – and is a great return on your time invested.
There’s no reason why you can’t go ahead and put into practice the ideas I’ve shown you in your next one-to-one or team meeting. If you’re interested, and would like some support in how to coach effectively, then I’d suggest two options. You could learn by being coached yourself, or you could find some training on coaching skills.
If you want to get the most from your people, if you want to help them develop, then coaching is a great skill to use – as after all, personal growth takes place at the intersection of ownership, accountability, support and challenge – and that is what a good coach provides.
Eszter Molnar Mills is a highly experienced and qualified leadership coach, and has taught coaching skills to hundreds of managers. Eszter and her team at Formium Development provide training and support to managers so they can get the best out of themselves, their teams and their organisations.
How we can help you
Coaching: if you’re looking for someone to help you to find solutions for your goals, we have a number of coaches available for phone/video conference coaching. Click here for more details.
Training: if you want more help on using a coaching approach as part of your management toolkit, then get in touch about our in-house workshops on Coaching Skills for Managers.
Webinar: People who join up to our newsletter get access to a bunch of helpful information and resources. This includes periodic access to our webinar on Coaching.
Do you want more articles like this?